Android Qt projects require AndroidManifest.xml file for a a number of reasons, including the definition of required permissions and so on. Creating this file on the other hand, and adding it to your Android Qt project requires a few strict instructions that are provided in this post.
First things first, I’ve used Qt Creator 4.9.1 and Android for armeabi-v7a (Clang Qt 5.12.3 for Android ARMv7) to create the screenshots and example code snippets in this post, so if you’re using a different versions (especially old versions) then you should expect some discrepancies.
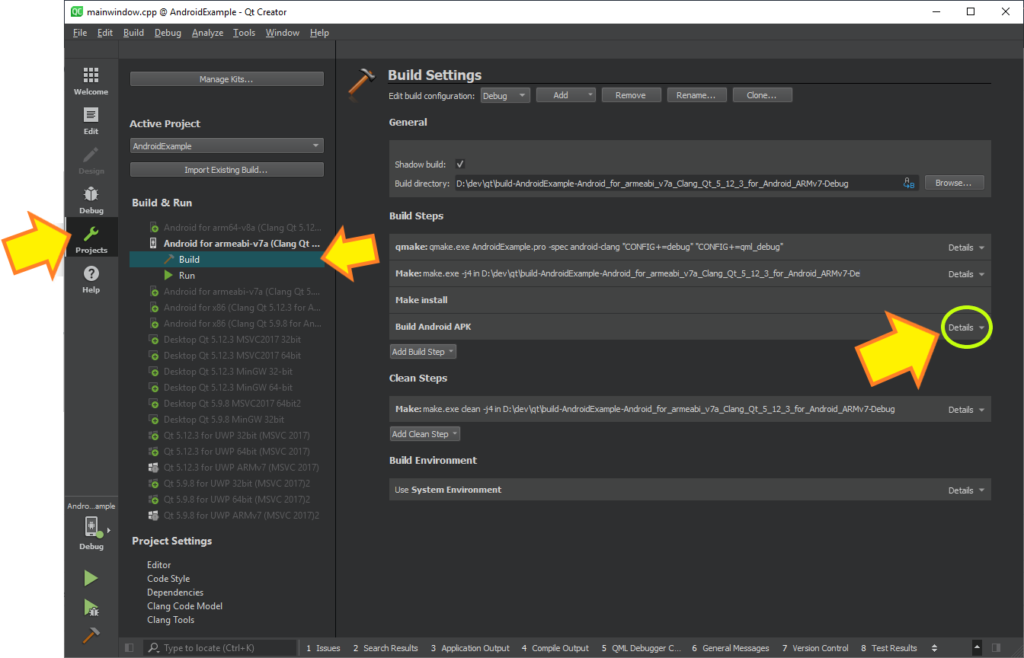
After creating your project (let’s assumed it’s called AndroidExample), you must switch to Projects mode first. This can be done by pressing CTRL+5 or by using the Toolbar at the left side in Qt Creator as seen in the following picture:
As it can be seen in the preceding picture, from Build & Run, you need to choose the right Qt Kit, then choose Build and expand Build Android APK under Build Steps group.
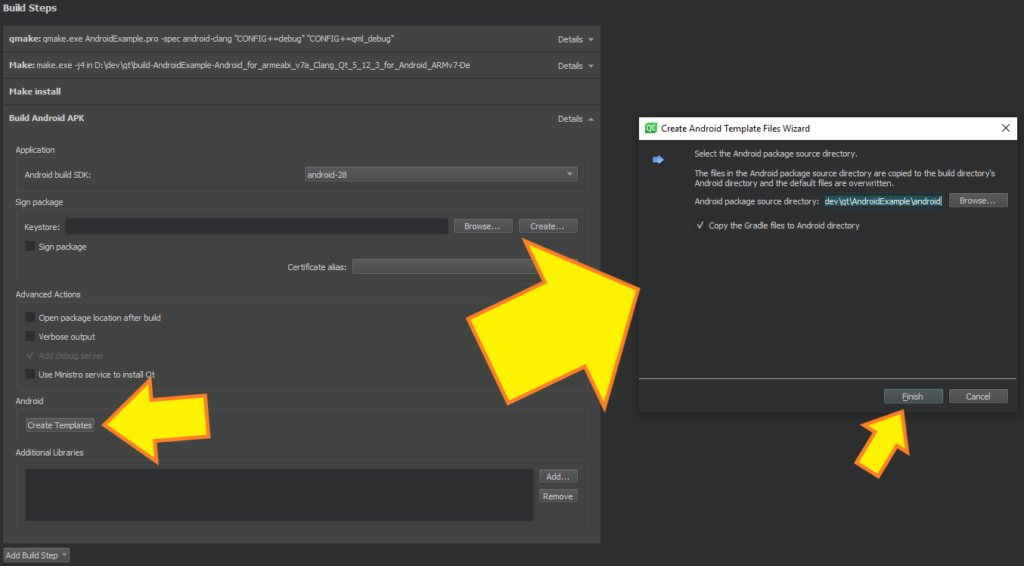
The only thing that remains is to actually create AndroidManifest.xml and add it to your Android Qt project. For this reason you just need to click on Create Template button and in the Create Android Template Files Wizard you have to press Finish, leaving all options as they are.
Here is a screenshot depicting the same:
Doing so will add a number of files to your project including AndroidManifest.xml and it will cause your project *.pro file to be updated with the following entries:
DISTFILES += \
android/AndroidManifest.xml \
android/build.gradle \
android/gradle/wrapper/gradle-wrapper.jar \
android/gradle/wrapper/gradle-wrapper.properties \
android/gradlew \
android/gradlew.bat \
android/res/values/libs.xmlIn addition to the preceding entries, something similar to the following will also be added to the *.pro file which is required in order for your project to actually treat the newly added files as Android files:
ANDROID_PACKAGE_SOURCE_DIR = $$PWD/androidYou can now start editing the AndroidManifest.xml according to your needs and how you want your project to behave.